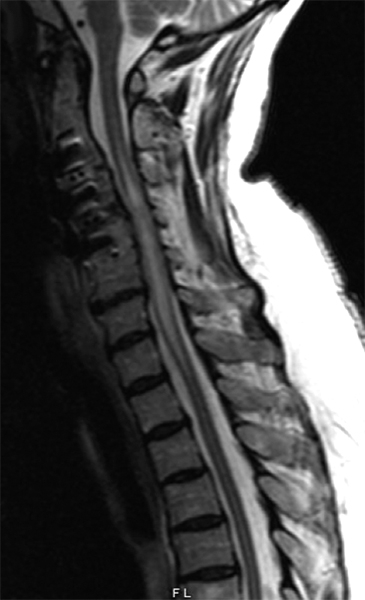
Q7: A 75-year-old woman with history of prior cervical spine decompression presented with progressive neck pain, asymmetric hand tingling, and neuropathic pain, followed by urinary incontinence and gait difficulty. Sagittal T2 weighted imaging likely shows?.
 |
