-
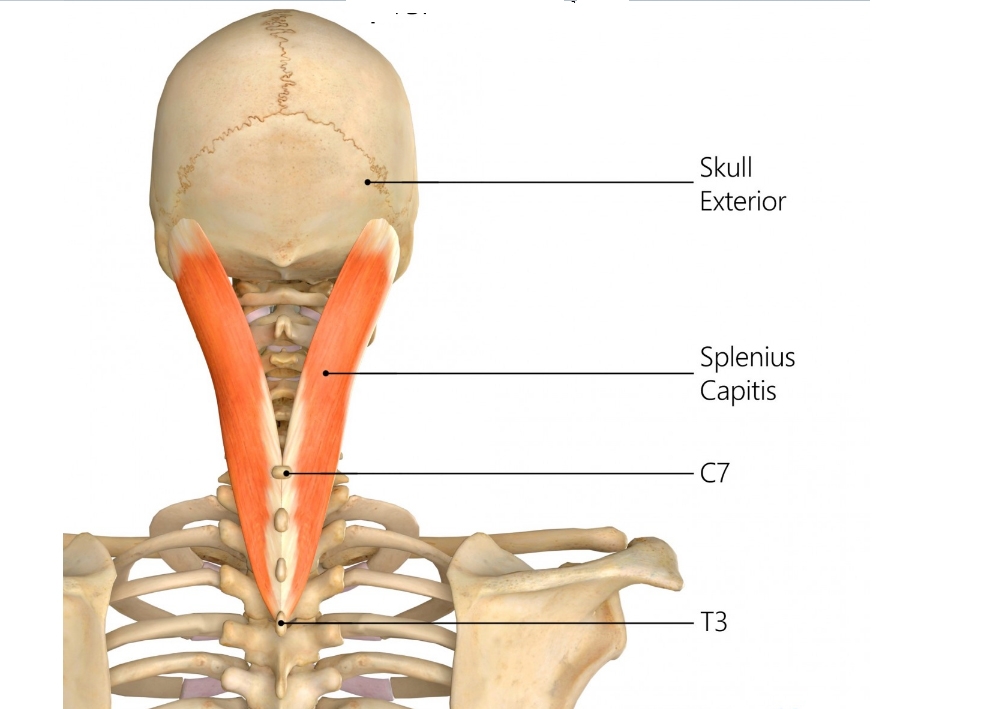
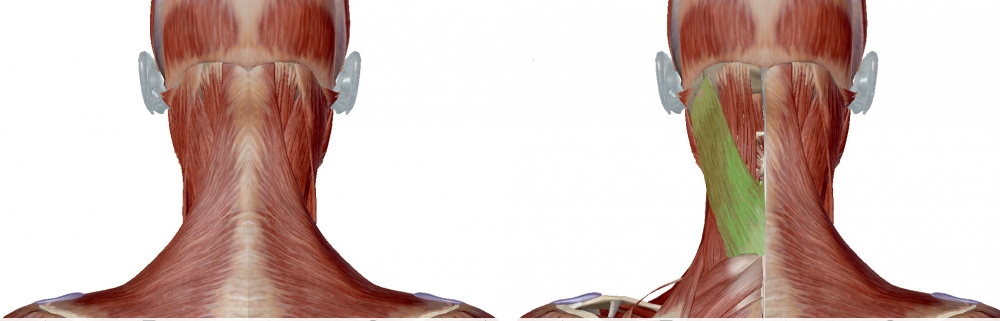
Origin: nuchal ligament and spinous processes of seventh cervical vertebra (C7) and upper three or four thoracic vertebrae (T1–4)
-
Insertion: posterior aspect of mastoid process of temporal bone. Lateral part of superior nuchal line, deep to attachment of sternocleidomastoid.
-
Action:
Acting on both sides: extends head and neck.
Acting on one side: tilts neck to the same side; rotates head to same side as contracting muscle (ipsiversion).
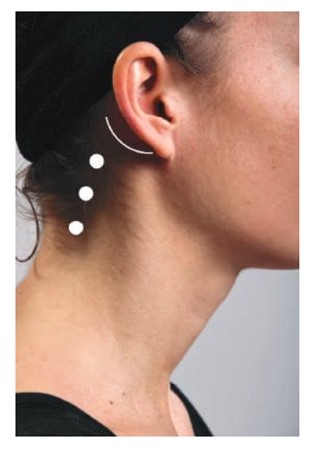
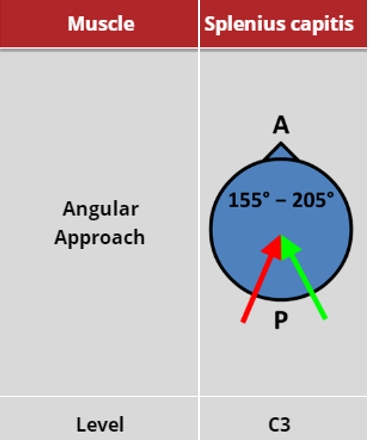
Locate the mastoid process (marked with the semicircle in the image (Surface Anatomy: injection sites for Splenius muscle) and the border of the sternocleidomastoid. Posterior to the sternocleidomastoid is the splenius capitis, and the initial injection is given there. The length of the muscle is followed diagonally backwards and downwards, and the second injection given. If no EMG activity is heard, the muscle may be activated by asking the patient to turn their head to the ipsilateral side.
|
 |
|
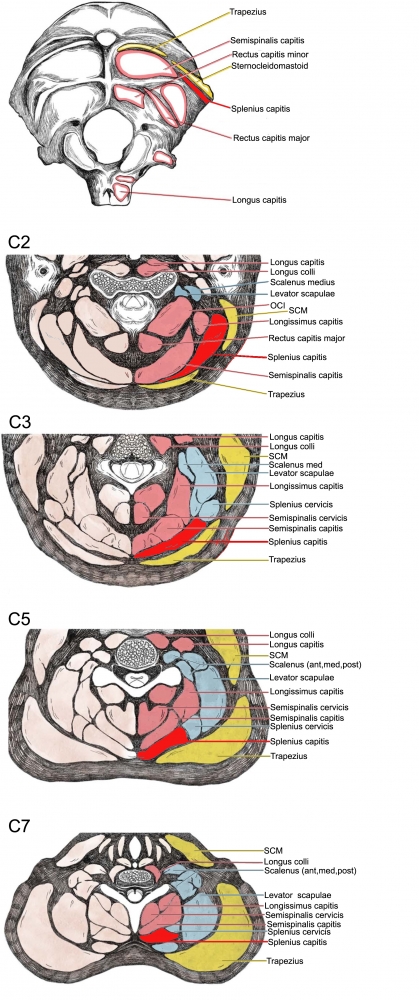
Figure 10. Trajectory of approach and relationships of the surrounding muscles to Splenius capitis
|
|
 |
 |

From: Fietzek UM, Nene D, Schramm A, Appel-Cresswell S, Košutzká Z, Walter U, Wissel J, Berweck S, Chouinard S, Bäumer T. The Role of Ultrasound for the Personalized Botulinum Toxin Treatment of Cervical Dystonia. Toxins (Basel). 2021 May 20;13(5):365.
(vv)Splenius.mp4(tt)
 |
 |

