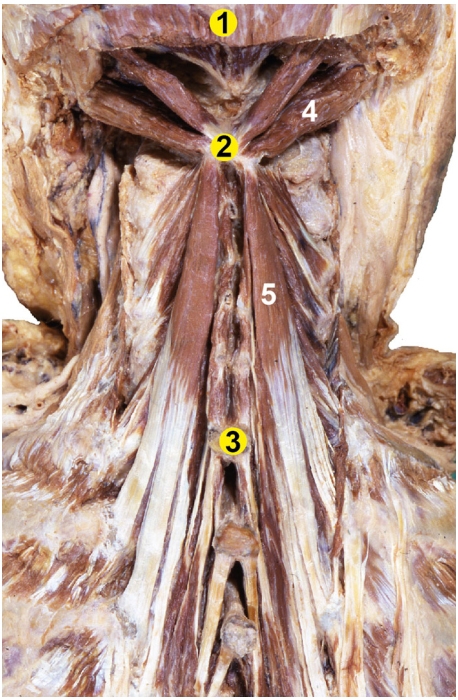
-
Origin: Transverse processes of T1-T6
-
Insertion: Spinous processes of C2-C7
-
Action: Bilateral contraction leads to extension of the neck.
Unilateral contraction causes lateral flexion ipsilaterally and contralateral rotation.
 |
 |


From: Fietzek UM, Nene D, Schramm A, Appel-Cresswell S, Košutzká Z, Walter U, Wissel J, Berweck S, Chouinard S, Bäumer T. The Role of Ultrasound for the Personalized Botulinum Toxin Treatment of Cervical Dystonia. Toxins (Basel). 2021 May 20;13(5):365.
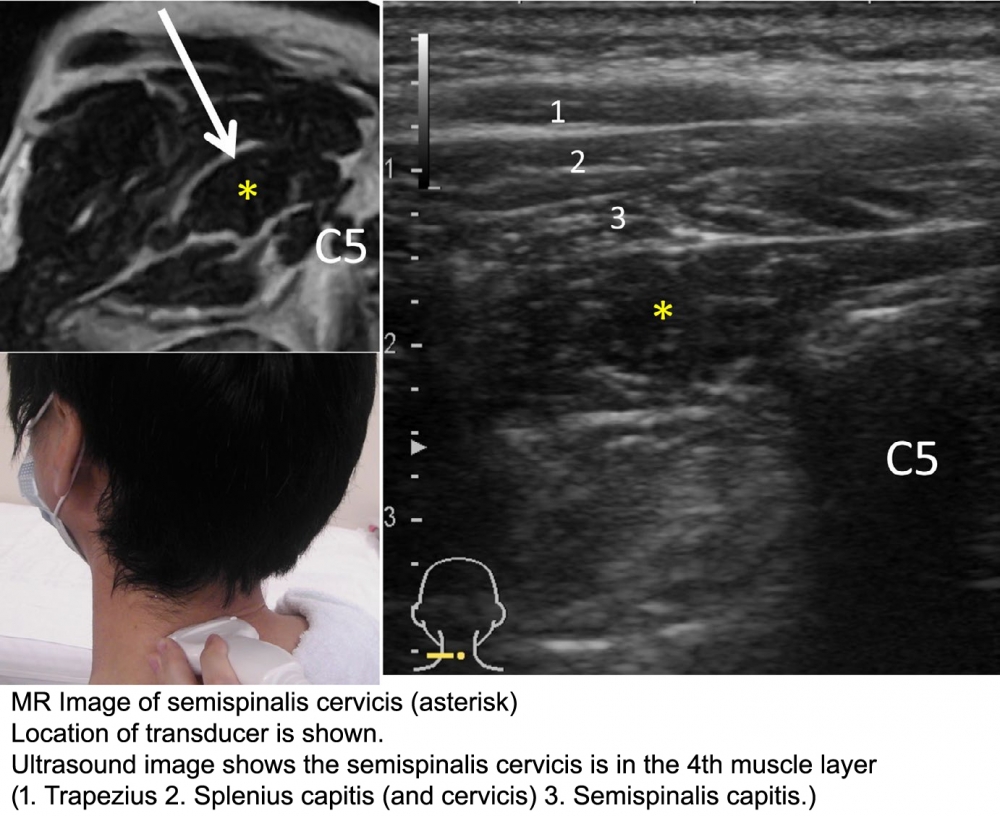
Technique: (from: Mezaki T. Ultrasoundâ€guided botulinum toxin therapy for deep muscles in cervical dystonia. Neurol Clin Neurosci 2020; 8: 3–10)
1. Place the linear transducer on the posterior aspect of the neck horizontally at the level of the posterior spinous process of the fifth cervical (C5) vertebra.
2. The muscle is found deep within the muscle layers of the neck: from superficial to deep, the layers consist of the trapezius, the splenius capitis (and cervicis), the semispinalis capitis, and then the semispinalis cervicis are identified. (Deep to this muscle, there is the multifidus muscle)
3. Compare the muscle thickness between both sides. Since the contribution of this muscle for head rotation is usually minor, a small difference may be ignored.
4. Inject botulinum toxin above and below the C5 level, 3â€4 centimeters apart. The convenient needle size is 27 gauge, length of 38 mm.