-
Origin: posterior surface of transverse processes of T1 to T6, and the articular processes of the lower four cervical vertebrae
-
Insertion: posterior margin of mastoid process and the temporal bone. The insertion is deep to that of the sternocleidomastoid and splenius muscles.
-
Action: Acting bilaterally, extends and hyperextends head
Acting unilaterally, flexes and rotates the head ipsilaterall (ipsiversion). The rotation is ipsilateral, and rotation of the head takes place at the atlanto-axial joint.
The muscle is deep to the levator scapulae muscle at the C5 level, and its depth greatly varies from patient to patient, being unexpectedly superficial in some adults.
Longissimus capitis acting bilaterally will extend the vertebral column (acting unilaterally flexes the head and neck laterally).
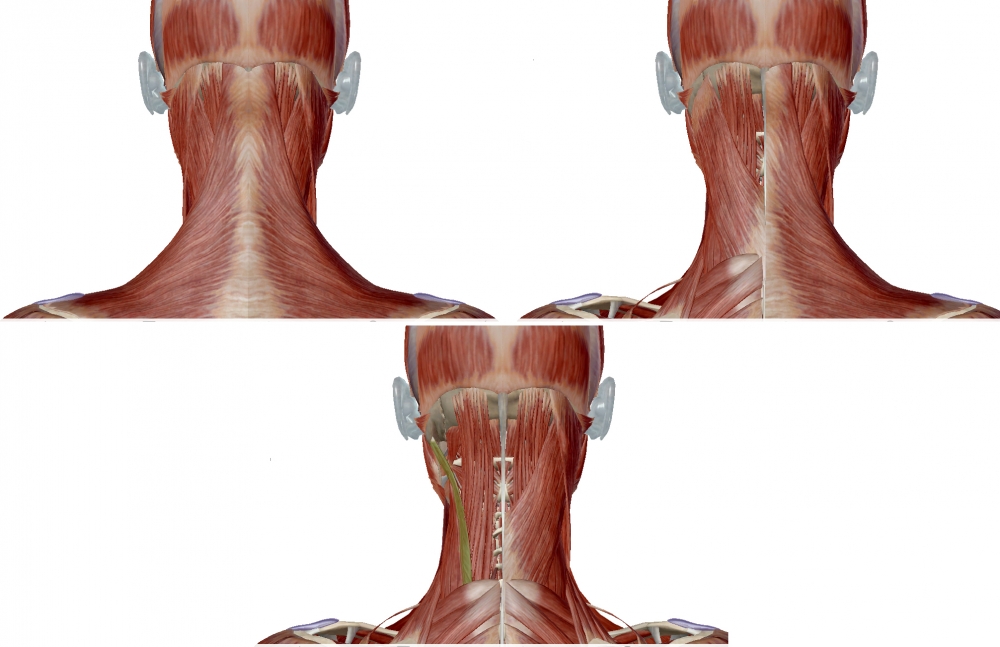
Note that in the figure on the right, splenius capitis is transparent, allowing for the longissimus capitis to be seen deep to splenius.
The longissimus capitis lies between the longissimus cervicis (which is directly lateral to it) and the splenius capitis (which is directly medial to it).
 |
 |

 |
 |
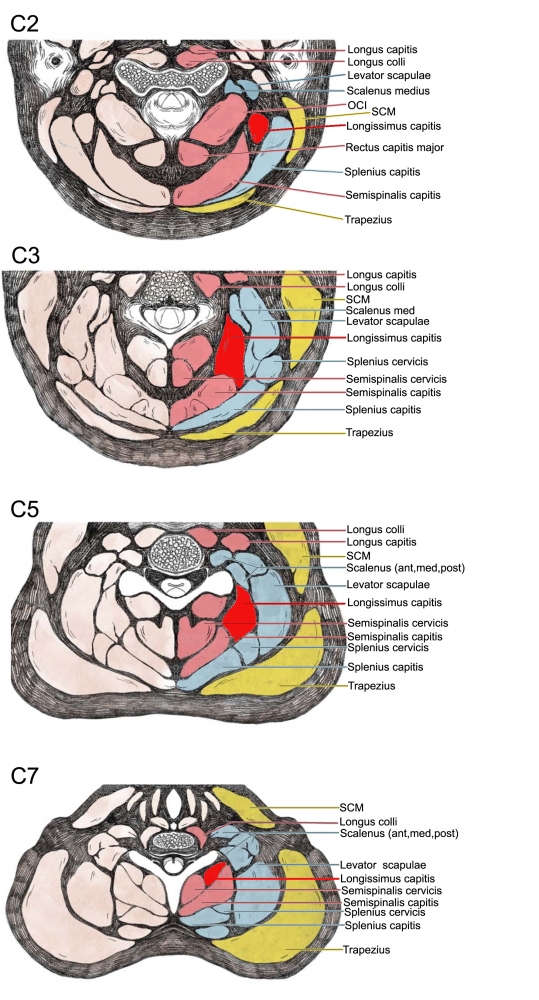

From: Fietzek UM, Nene D, Schramm A, Appel-Cresswell S, Košutzká Z, Walter U, Wissel J, Berweck S, Chouinard S, Bäumer T. The Role of Ultrasound for the Personalized Botulinum Toxin Treatment of Cervical Dystonia. Toxins (Basel). 2021 May 20;13(5):365.
Ultrasound Technique
1. Palpate the spinous process of the axis and move the operator's finger to the third cervical (C3) spinous process.
2. Place the linear transducer horizontally at this level over the triangle formed posteriorly by the trapezius, anteriorly by the sternocleidomastoid, and inferiorly by the middle third of the clavicle.
3. Move the transducer a little dorsally and localize the transverse process of C3 on the right lower part of the screen. The longissimus capitis muscle can be seen in the direction of 10â€11 o'clock from the transverse process with a deformed and widened letter Dâ€chape (the vertical line of the letter D represents the fascia, discriminating it from the semispinalis capitis muscle)
4. After the injection, repeat the procedure at the C5 level. Color Doppler imaging at this level occasionally detects an artery, which is the superficial branch of the transverse cervical artery.
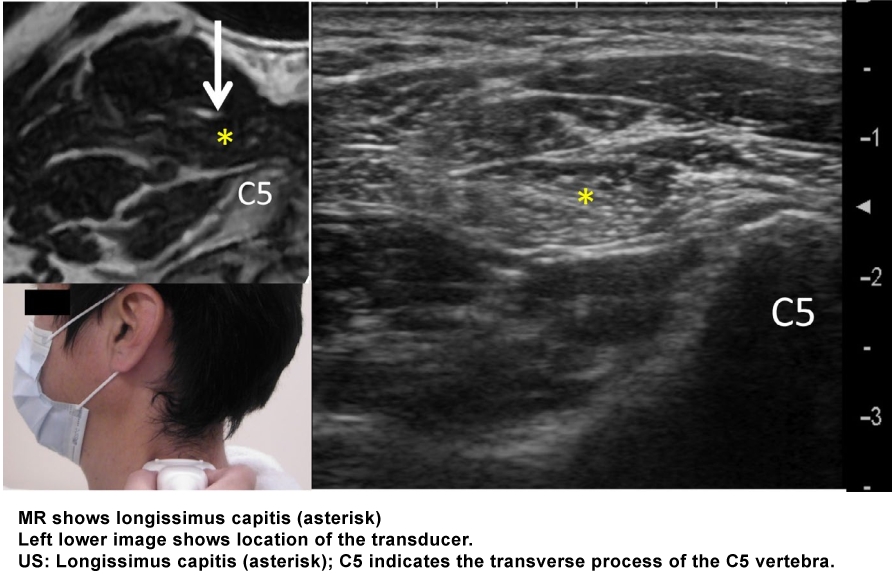
From: Mezaki T. Ultrasoundâ€guided botulinum toxin therapy for deep muscles in cervical dystonia. Neurol Clin Neurosci 2020; 8: 3–10.

